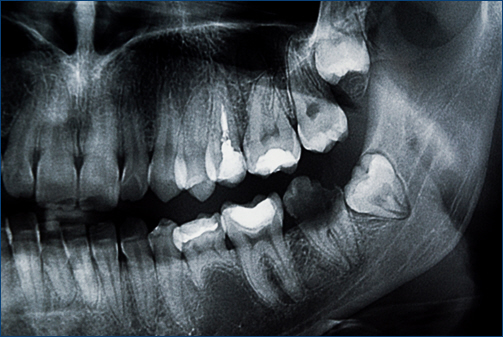
Impacted teeth are teeth that have not erupted properly and are stuck beneath the gum line or against other teeth. This condition is most commonly associated with wisdom teeth, but can also affect other teeth, such as canines. An impacted tooth can cause discomfort, misalignment, and other dental issues if not addressed promptly. Understanding the treatment options and what to expect during the process can help you make informed decisions about your oral health.
Causes and Symptoms
-
- Causes: Impacted teeth are often caused by a lack of space in the jaw for new teeth to emerge properly. Genetic factors, such as jaw size and the natural alignment of teeth, can also contribute to impaction. Additionally, overcrowding due to the presence of extra teeth or retained baby teeth can prevent normal eruption.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of impacted teeth include swelling and tenderness around the gums, difficulty opening the mouth, bad breath, and pain or discomfort in the jaw or ear. In some cases, impacted teeth may not cause noticeable symptoms, making regular dental check-ups important for early detection.
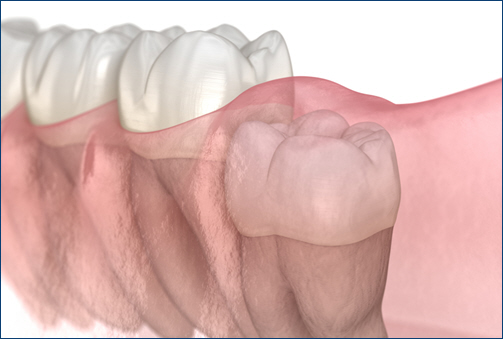 Treatment Options
Treatment Options
-
- Observation and Monitoring: If an impacted tooth is not causing pain or affecting other teeth, your dentist may recommend regular monitoring. This approach is suitable for teeth that are unlikely to cause problems, particularly in older adults who have adapted to the condition.
- Surgical Extraction: The most common treatment for them, especially wisdom teeth, is surgical extraction. This procedure involves removing the tooth to alleviate pain, prevent infection, and avoid damage to surrounding teeth. It is typically performed under local anesthesia, and recovery time varies depending on the complexity of the extraction.
- Orthodontic Treatment: For impacted canines or other teeth that play a crucial role in dental alignment, orthodontic treatment may be necessary. Braces or other orthodontic appliances can help guide impacted teeth into their correct position over time. This treatment is often used in combination with surgical exposure of the impacted tooth.
What to Expect During Treatment
-
- Preparation: Before undergoing treatment for an impacted tooth, your dentist or oral surgeon will conduct a thorough examination, which may include X-rays to assess the position and condition of the impacted tooth. They will discuss the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes with you.
- Procedure and Recovery: Surgical extraction is usually performed in a dental office or surgical center. The recovery process involves managing swelling and discomfort with prescribed pain relievers and cold compresses. You will need to follow post-operative care instructions, such as avoiding certain foods and activities, to ensure proper healing.
- Follow-Up Care: After treatment, regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing and address any complications. Your dentist may recommend additional treatments, such as orthodontics or dental restorations, to maintain optimal oral health.
Dealing with impacted teeth requires careful consideration and appropriate treatment to prevent long-term dental issues. Whether through monitoring, surgical extraction, or orthodontic intervention, addressing them is crucial for maintaining a healthy, functional smile. Consult with your dentist or oral surgeon to explore the best treatment options for your specific situation and ensure the health and alignment of your teeth. Regular dental check-ups and proactive care can help you manage impacted teeth effectively and prevent complications.